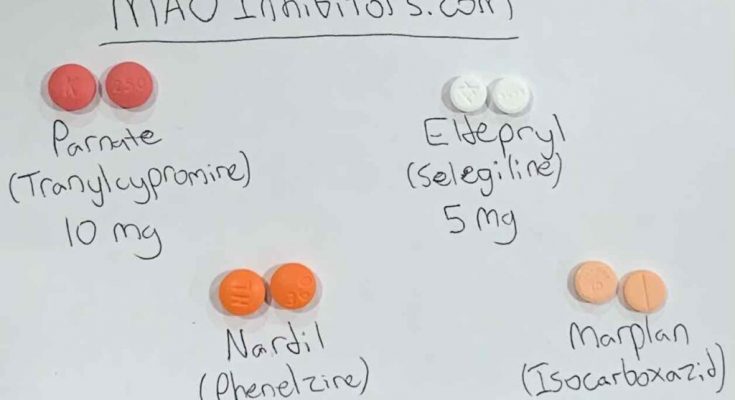
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a different class from various other antidepressants, dealing with various forms of depression as well as other nerve conditions such as social fear, panic disorder, as well as depression with irregular functions. Even though MAOIs were the first antidepressants presented, they are not the first choice in treating psychological health and wellness conditions due to numerous side effects, nutritional constraints, as well as security issues. MAOIs are only a therapy choice when all other medications are not successful. This task will highlight the device of action, pharmacology, unfavorable occasion account, tracking, as well as pertinent communications of MAOIs, essential for members of the interprofessional team in treating individuals with conditions where this drug course has a therapeutic function.
To get a deeper look at MAOIs, please follow the page https://maoinhibitors.com/mao-inhibitor-guide/.
Indications
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors were initially presented in the 1950s. They are a different class from various antidepressants, treating various types of anxiety in addition to other nervous system problems such as a panic attack, social phobia, and clinical depression with irregular functions. Examples of atypical attributes are eating and sleeping way too much. Even though MAOIs were the initial antidepressants presented, they are not the first choice in treating mental health disorders as a result of a number of negative effects, nutritional constraints, as well as safety issues. MAOIs are only a treatment option when all various drugs are unsuccessful.
Moreover, instances of neurological disorders that can take advantage of MAOIs endure Parkinson’s illness and those identified with numerous system atrophy. Numerous system degeneration is a neurodegenerative disease that consists of signs impacting motion as well as high blood pressure.
System of Action
Monoamine oxidase preventions are responsible for obstructing the monoamine oxidase enzyme. The enzyme monoamine oxidase breaks down various kinds of natural chemicals from the mind: serotonin, norepinephrine, tyramine, as well as dopamine. The inhibition of the breakdown of such neurotransmitters via MAOIs, thus, boosts their levels as well as allowing them to remain to influence the cells that have been influenced by depression. There are two types of monoamine oxidase, A as well as B. The MOA A is primarily distributed in the intestine, placenta, and liver, but MOA B exists in the liver, brain, and platelets. Noradrenaline and serotonin are the substitutes of MOA A; however, methylhistamine, phenylethylamine, and tryptamine are substitutes of MOA B. Tyramine and dopamine are metabolized by both MOA A and MOA B. Selegiline as well as rasagiline are irreparable and discerning preventions of MAO type B, however, safinamide is relatively easy to fix as well as careful MAO B prevention. MAOIs are permanent or reversible. Moclobemide is an example of a reversible MAOI I or RIMA, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, as well as selegiline irreversibly hinder MOA. Selegiline in reduced doses is a selective, irreparable MAO B inhibitor, but it is no longer selective at higher dosages.